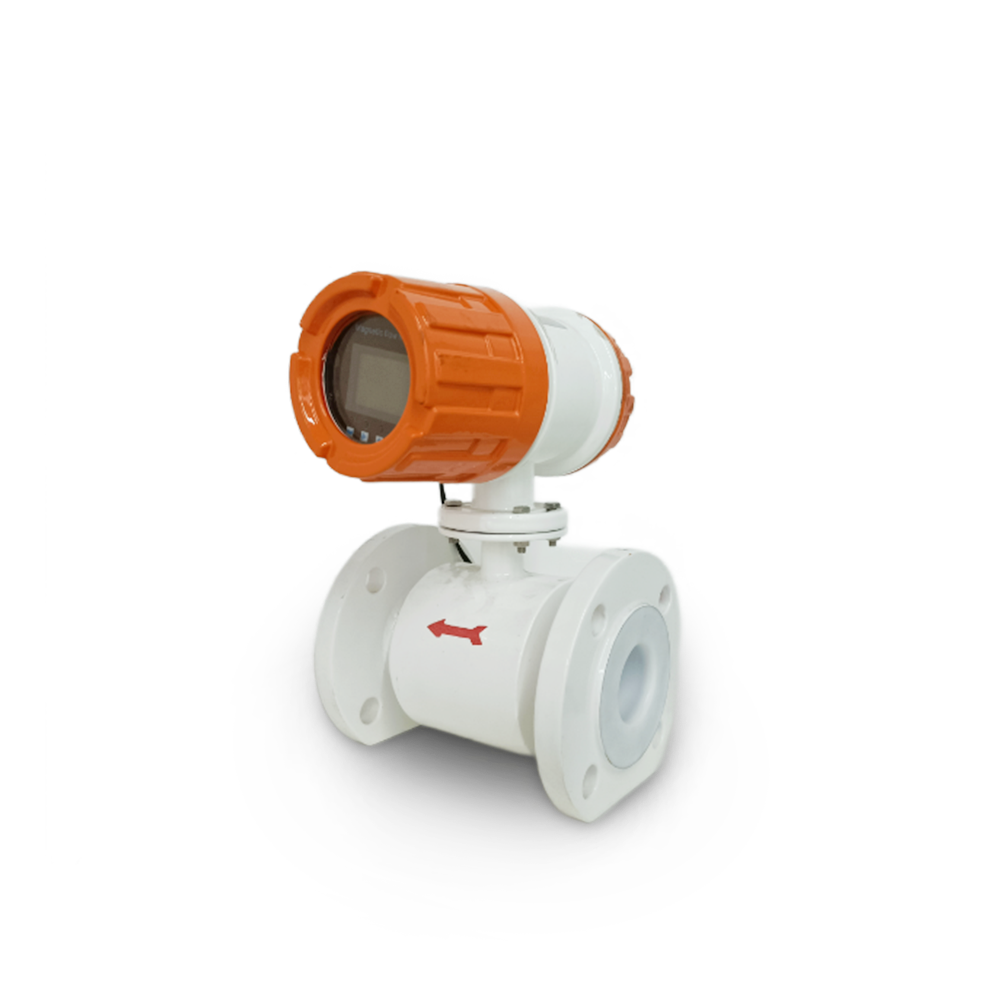
Electromagnetic Flowmeters: Working Principle, Components, Applications, and Installation Tips
From: Issued date 2025.05.29 Back
Working Principle
An electromagnetic flowmeter operates based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.When a conductive liquid flows through a magnetic field in a non-conductive measuring tube,it generates an induced voltage.Two electrodes installed perpendicular to both the magnetic field and flow direction detect this voltage.The magnitude of the induced voltage is directly proportional to the flow rate,enabling accurate and reliable fluid measurement across a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Main Components
1.Coil
The excitation coil generates a magnetic field through which the conductive fluid flows.The design and stability of the magnetic field are critical for accurate measurement.For example:
In firefighting systems,where water flow must be measured quickly and reliably under emergency conditions,the magnetic field must remain stable even under pressure fluctuations.
For cooling water and air conditioning water systems,precise flow measurement helps optimize energy efficiency and system control.
2.Electrodes
The electrodes detect the voltage induced by the moving conductive liquid.The material selection is critical for different media:
Stainless steel or titanium electrodes resist corrosion in seawater,hot water,and slightly acidic media.
For highly corrosive liquids like nitric acid,sulfuric acid,hydrochloric acid,and sodium hydroxide,specialized electrodes such as Hastelloy or platinum-iridium are recommended to maintain long-term stability and accuracy.
3.Liner
The liner provides insulation and protects against chemical attack:
PTFE(Teflon)liners are ideal for chemical media like ammonia,urea,potassium nitrate,and milk,which require hygienic and corrosion-resistant materials.
Rubber or polyurethane liners are used in wastewater,slurry,and pulp applications,where resistance to abrasion and fouling is critical.
EPDM or Neoprene linings are suitable for mineral water,cooling water,and air conditioning systems,ensuring non-contamination and long service life.
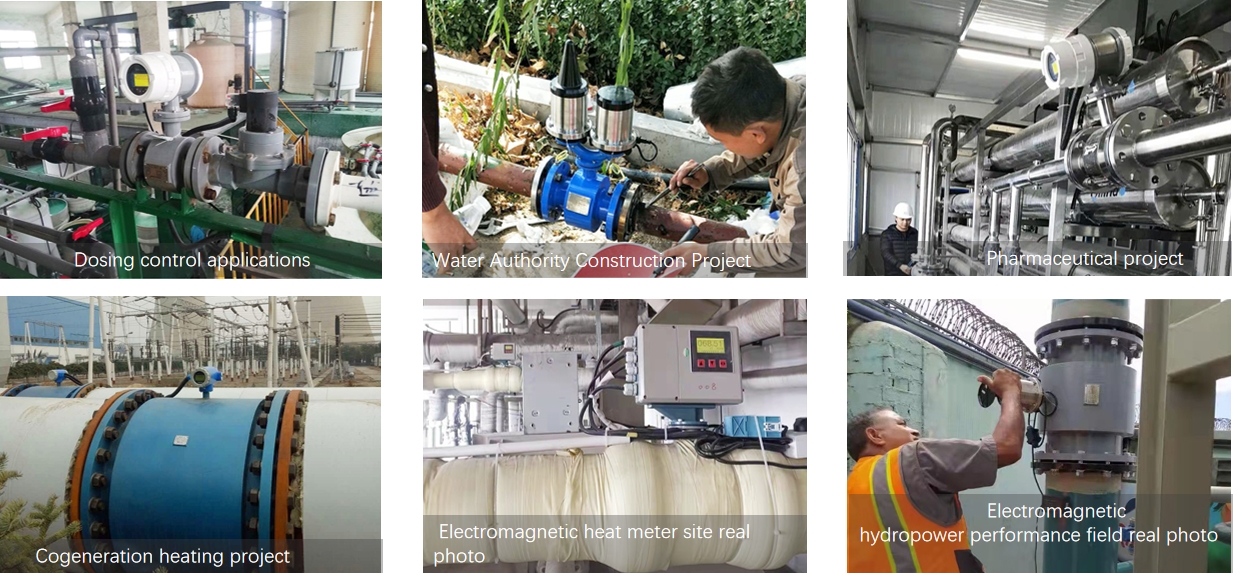
Application Media Overview
Electromagnetic flowmeters are highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of conductive fluids:
Application Medium | Flowmeter Suitability&Benefits |
Mineral water | Hygienic,non-reactive materials ensure purity. |
Wastewater | Handles suspended solids and high flow variability. |
Firefighting water | Reliable flow under high-pressure and emergency response conditions. |
Hot water | Temperature-resistant linings and stable performance. |
Cooling water | Precise monitoring for industrial cooling loops. |
Air conditioning water | Efficiency monitoring in HVAC systems. |
Seawater | Corrosion-resistant electrodes and liners. |
Nitric acid/Sulfuric acid/Hydrochloric acid | Requires chemical-resistant materials(e.g.,PTFE liner,Hastelloy electrodes). |
Sodium hydroxide | Alkaline compatibility for accurate dosing and monitoring. |
Ammonia/Urea | Chemical process control and dosing accuracy. |
Pulp/Slurry | Abrasion-resistant designs for thick,particulate-laden flows. |
Potassium nitrate | Fertilizer process monitoring. |
Milk | Food-grade sanitary flowmeter options available. |
Selection Guidelines
To select the right electromagnetic flowmeter,follow these steps:
Confirm Fluid Conductivity:Must be above the minimum threshold(typically>5µS/cm).
Check Medium Compatibility:
Use PTFE liners and Hastelloy electrodes for strong acids(e.g.,sulfuric,nitric).
Use rubber liners for slurry,pulp,and wastewater.
Use sanitary-grade materials for milk and mineral water.
Consider Pressure:If working pressure is provided,calculate rated pressure as 1.5x working pressure.
Match Temperature Range:Based on the lining and installation environment.
Verify Flow Range and Pipe Size:Ensure the flowmeter matches both the expected flow rate and the pipe diameter.
Specify Protection Rating:For outdoor or submerged use,choose IP68-rated units.
Explosion-Proof Requirements:Use sand-filled meter body and explosion-proof converter in hazardous environments.
High-Pressure or Customized Connections:May require additional costs and engineering review.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is essential to maintain accuracy:
Avoid Extreme Heat or Sunlight:Prevent overheating of the coil and electronics.
Keep Away from Magnetic Interference:Do not install near high-powered motors or welding machines.
Prevent Vibration:Mount securely to a stable foundation.
Install with Correct Flow Direction:Align with the arrow indicated on the flowmeter body.
Avoid High Points in Piping:Prevent air pockets that affect readings,especially in systems handling slurry,milk,or firefighting water.
Ensure Full Pipe Conditions:The flowmeter must always operate in a fully filled pipe for accurate measurement.
Ideal Position:Mount at the lowest point of a horizontal pipeline to maintain full-pipe condition.
Common Faults and Troubleshooting
1.Improper Installation
Installed at the highest point may trap air(especially in hot water or milk applications).
Incorrect orientation(e.g.,downward vertical pipe)may cause empty pipe errors.
2.Environmental Interference
Stray currents in wastewater or industrial plants can affect accuracy.Use proper grounding.
Magnetic field interference from motors and transformers can disrupt measurement.Ensure adequate shielding.
3.Lightning Strikes
Surges from power lines or signal lines can damage electronics.Use surge protection and isolate communication wiring.
4.Variable Field Conditions
During startup,conditions may be stable,but later external welding,chemical process changes,or new equipment can cause output signal fluctuations.Recheck grounding and isolation.

Our electromagnetic flowmeters are designed to handle a wide variety of conductive media ranging from clean water to aggressive chemicals and high-viscosity slurries.Proper material selection,installation,and grounding ensure long-term accuracy and durability.